A review of Bariatric Surgery Options
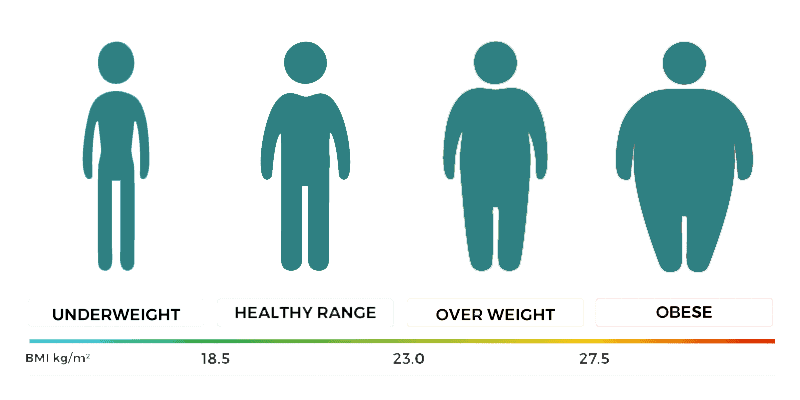
There are over 1.9 billion obese or overweight adults in the world today. Obesity leads to excess body fat accumulation. It causes severe health problems, such as heart diseases, sleep apnea, and diabetes.
There are different ways to manage the condition, including changing your diet, exercising, and bariatric surgery. Doctors perform bariatric surgery to help you lose excess weight. They change the structure of the digestive system to limit the amount of food that you can take. It is effective in lowering death rates in people with severe obesity.
However, some risks accompany the procedure. Therefore, doctors only use it where:
- You have a BMI (body mass index) above 35 and have obesity-related issues, such as sleep apnea.
- You weigh over 100 pounds
- All conventional methods have failed to work
- You can change your diet so that the surgery is successful and to prevent post-surgery complications.
Before you decide to have bariatric surgery, talk to your doctor to know which procedure is best for you. Here is a review of the four types of bariatric surgeries available today.

1. Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass)
It is one of the most common types of bariatric surgery, and it is non-reversible. It is a complex process that may require you to stay in the hospital for extended periods for close monitoring. The aim is to decrease the amount of food that you can eat and the nutrients you absorb. They call the process malabsorption.
Doctors will separate a part of your stomach from the rest during the surgery, creating a small pouch. The food enters the small pouch, which can only hold a tiny amount of food to seal the rest off. It makes you eat a tiny portion of food.
They then connect the small pouch to the small intestine so that the food moves directly to the small intestine’s middle part from the pouch. The small intestine cannot digest food well, forcing your body to absorb fewer nutrients than when you digest the food thoroughly.
The procedure helps you to lose a lot of weight. However, you need to choose what you eat carefully to prevent cases of essential nutrient deficiency. Therefore, you must make long-term diet changes to incorporate foods high in significant nutrients that your body requires.
People with severe reflux disease, diabetes, and very high BMI will benefit more from this procedure.
Benefits
- It enables you to lose weight faster, with the significant loss occurring in the first six months.
- Rerouting the gastrointestinal tract helps change your hormones positively, increasing the chances of improving specific health conditions, such as diabetes, high cholesterol, and heartburn.
- Has long-term positive effects
Disadvantages
- You risk losing essential nutrients like calcium and iron, leading to malnutrition.
- May cause dumping syndrome as the food passes quickly from the stomach to the intestine.
2. Sleeve Gastrectomy
It is the most recent form of bariatric surgery. Doctors remove about 85% of your stomach before stapling the remaining part, forming a long tube-shaped pouch. It is a restrictive procedure, as it limits the amount of food that you can eat.
Also, it leads to the production of less ghrelin hormone, which regulates your appetite, resulting in decreased appetite and food cravings. The decrease in ghrelin hormone also results in faster satiation.
It is less invasive than gastric bypass, so you do not have to stay for an extended period in the hospital.
People who can benefit more from this procedure include:
- Those who have had over one abdominal surgery as they operate on the upper section of your abdomen, which does not have severe scarring.
- High-risk surgical patients
- Those with multiple medical medications for psychiatric conditions
Benefits
- Has lower risks than gastric bypass
- It does not affect food absorption, so you cannot have a nutrient shortage.
- Reduces food cravings
- Has long-term benefits
Disadvantage
It is irreversible
3. Adjustable Gastric Band
Doctors place an adjustable silicone band around the upper section of the stomach, reducing the food you can eat. A narrow channel connects the two parts that allow food to flow from the upper to the lower. It also reduces the feeling of hunger.
Unlike the first two, the band is adjustable, so doctors can change the tightness to enable you to reduce or increase the amount of food you consume.
Benefits
- It is simpler and safer than sleeve gastrostomy or gastric bypass. You can be sure it is one with the lowest rate of complications.
- Less invasive
- Lower risk of developing malnutrition problems
- It is reversible
Disadvantages
- You experience less weight loss than with the other surgeries.
- You may regain the weight loss with time if the band loosens.
- People who go for this surgery have the highest tendency to go for subsequent surgeries.
4. Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS)
BPD/DS or duodenal switch surgery occurs in two stages. In the first stage, the doctor removes part of the stomach like in sleeve gastrectomy. The second step involves the removal of parts of the small intestine to reduce the amount of food that you can absorb. They then connect the remaining section of the intestine to the duodenum near the stomach, bypassing much of the intestine.
The BPD/DS procedure results in you having a smaller stomach and a shorter intestine. As a result, it limits weight gain, as you can only eat small food portions and absorb very little of it. Therefore, the procedure leads to the highest weight loss than the others.
This procedure is an excellent choice if you have severe obesity, severe metabolic disease, and you can follow the doctor’s orders to the letter.
Benefits
- It has a higher and faster rate of weight loss, making it an excellent choice for those dealing with weight-related issues.
- No dietary restrictions, so you can eat everyday foods.
Disadvantages
- Has the highest rate of complications and death
- It may lead to severe malnutrition and vitamin deficiency
- Needs frequent follow-up visits with the doctor
Risks of the Surgery
Getting the surgery exposes you to some health risks, both long-term and short-term. Some of these risks include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Breathing problems
- Blood clots
- Gastrointestinal leakage
- Bowel obstruction
- Dumping syndrome
- Hernias
- Vomiting
- Acid reflux
- Low blood sugar
Conclusion
To qualify for bariatric surgery, you’ll have to undergo screening to ensure you meet minimum requirements. You must be ready to adopt a healthier lifestyle. Otherwise, the risks of the surgery may be severe. Also, you may have to undergo monitoring to ensure you comply with the conditions given by the doctor.
If you intend to have bariatric surgery, talk to your insurance provider to determine if your policy includes it, as the procedures are expensive.